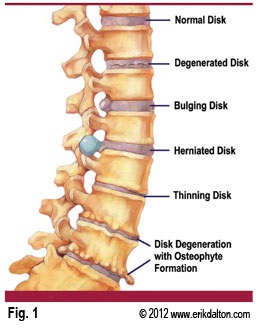
Note the difference between a bulging disc and a herniated disc.
What is an Intervertebral Disc?
Between each vertebra in the spinal column sits a shock-absorbing disc. The disc consists of a tough outer coating, called the annulus fibrous, which surrounds the inner gel-like nucleus pulposus.
What is a Herniated Disc?
A disc herniation can sometimes be called a “slipped disc”. While a disc can’t really “slip” out of place, it sure may feel that way.
When a herniation occurs, the nucleus pulposus escapes through a break in the annulus fibrosus. The painful sensation associated with a disc herniation is actually due to the disc material leaking into chambers running up and down the spinal column. Often, this can compress or pinch nerves or the spinal column housed in those chambers.
What is a Bulging Disc?
A bulging disc occurs when the nucleus pulposus bulges against the annulus fibrosus. This bulging can deform the disc and cause it to press into the spinal column or nerves.
How to Avoid a Herniated Disc and Bulging Discs.
Activities that can increase your risk for disc herniation and bulging are similar to muscle strains and sprains. (see our article called “Strains and Sprains in Lower Back Pain“) Heavy lifting, bending forward and lifting while twisting, especially when done repetitively, increase your likelihood for disc herniation. Always be aware of your posture and be sure to lift with your legs, not your back. Be mindful of your body mechanics, especially if you’re inflexible or tight, and tone your abdominals slightly when lifting. Always maintain a long, strong core.
Symptoms of Herniated and Bulging Discs.
A major symptom of a disc herniation includes radiating pain and numbness in the extremities. Lower back pain that resolves after a couple of days, but is then followed by numbness and weakness in the legs and feet is indicative of a disc herniation.
Treatments for Disc Injuries.
Fortunately, many disc injuries heal, albeit slowly. Physical examination by your doctor accompanied by an MRI scan can definitively diagnose disc herniations and bulges. Over-the-counter anti-inflammatories are usually recommended to reduce pain initially, while physical therapy is sometimes required longer-term in the treatment for disc herniation. Gentle stretches and targeted exercises recommended by physical therapists can help reduce pressure on the nerve and alleviate pain. Learning proper posture and biomechanics while maintaining a long, strong core can help you heal (and avoid) disc injuries. And finally, receiving focused massage therapy treatments from an injury massage specialist can be very beneficial in helping to reduce muscle spasms, allowing your body to heal.
Contact our owner and Injury Specialist, David, with any of your injury questions at 303-444-1171. He has over 20 years experience working with injuries and athletes.
———
This blog is part of a series explaining lower back pain called, “Do You Have Lower Back Pain.”
